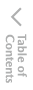Tire Information (U.S.A.)
Tire Labeling
Federal law requires tire manufacturers to place standardized information on the sidewall of all tires. This information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of the tire and also provides a tire identification number for safety standard certification and in case of a recall.
Information on Temporary Tires
Please refer to the sample below.

-
Temporary tires
-
Nominal width of tire in millimeters
-
Ratio of height to width (aspect ratio)
-
Diagonal
-
Rim diameter code
-
Load index & speed symbol
T115/70D16 90M is an example of a tire size and load index rating. Here is an explanation of the various components of that tire size and load index rating. Note that the tire size and load index rating may be different from the example.
T
Indicates a tire that may be installed on cars, SUVs, minivans and light trucks as designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA).
115
“115” is the nominal width of the tire in millimeters. This three-digit number gives the width in millimeters of the tire from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire.
70
“70” is the aspect ratio. This two-digit number indicates the tire's ratio of height to width.
D
“D” is the tire construction symbol. D indicates “diagonal ply construction”.
16
“16” is the wheel rim diameter in inches.
90
“90” is the Load Index. This two-or three-digit number indicates how much weight each tire can support.
M
“M” is the speed rating. The speed rating denotes the maximum speed for which the use of the tire is rated.
|
Letter Rating |
Speed Rating |
|---|---|
|
M |
81 mph |
Location of the Tire Label (Placard)
You will find the tire label containing tire inflation pressure by tire size and other important information on the driver's side B-pillar or on the edge of the driver's door frame.
SAMPLE

Tire Maintenance
Improper or inadequate vehicle maintenance can cause tires to wear abnormally. Here are some important maintenance points:
Tire Inflation Pressure
Inspect all tire pressure monthly (including the spare) when the tires are cold. Maintain recommended pressures for the best ride, top handling, and minimum tire wear. Use the pressures specified on the vehicle tire information placard or tire label for optimum service.
Tire Rotation
To equalize tread wear, rotate the tires every 16,000 km (10,000 miles) at the latest or sooner if irregular wear develops. Mazda recommends to rotate every 8,000 km (5,000 miles) to help increase tire life and distribute wear more evenly.

Do not include (TEMPORARY USE ONLY) spare tire in rotation.
Inspect the tires for uneven wear and damage. Abnormal wear is usually caused by one or a combination of the following:
-
Incorrect tire pressure
-
Improper wheel alignment
-
Out-of-balance wheel
-
Severe braking
After rotation, inflate all tire pressures to specification (Search) and inspect the lug nuts for tightness.
Rotate unidirectional tires and radial tires that have an asymmetrical tread pattern or studs only from front to rear, not from side to side. Tire performance will be weakened if rotated from side to side.
Replacing a Tire
Always use tires that are in good condition.
Driving with worn tires is dangerous. Reduced braking, steering, and traction could result in an accident.
If a tire wears evenly, a wear indicator will appear as a solid band across the tread.
Replace the tire when this happens.

-
New tread
-
Worn tread
-
Tread wear indicator
You should replace the tire before the band crosses the entire tread.
Tires degrade over time, even when they are not being used on the road. It is recommended that tires generally be replaced when they are 6 years or older. Heat caused by hot climates or frequent high loading conditions can accelerate the aging process. You should replace the spare tire when you replace the other road tires due to the aging of the spare tire. The period in which the tire was manufactured (both week and year) is indicated by a 4-digit number.
Refer to Tire Labeling (Search).
Safety Practices
The way you drive has a great deal to do with your tire mileage and safety. So cultivate good driving habits for your own benefit.
-
Observe posted speed limits and drive at speeds that are safe for the existing weather conditions
-
Avoid fast starts, stops and turns
-
Avoid potholes and objects on the road
-
Do not run over curbs or hit the tire against the curb when parking
If you feel a sudden vibration or ride disturbance while driving or you suspect your tire or vehicle has been damaged, immediately reduce your speed. Drive with caution until you can safely pull off the road. Stop and inspect the tire for damage. If the tire is under-inflated or damaged, deflate it, remove the tire and rim and replace it with your spare tire. If you cannot detect a cause, have the vehicle towed to the nearest vehicle or tire dealer to have the vehicle inspected.
Steps for Determining the Correct Load Limit
Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit-
-
Locate the statement “The combined weight of occupants and cargo should never exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs.” on your vehicle's placard.
-
Determine the combined weight of the driver and passengers that will be riding in your vehicle.
-
Subtract the combined weight of the driver and passengers from XXX kg or XXX lbs.
-
The resulting figure equals the available amount of cargo and luggage load capacity. For example, if the “XXX” amount equals 1400 lbs. and there will be five 150 lb passengers in your vehicle, the amount of available cargo and luggage load capacity is 650 lbs. (1400 - 750 (5 × 150) = 650 lbs.)
-
Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo being loaded on the vehicle. That weight may not safely exceed the available cargo and luggage load capacity calculated in Step 4.
-
If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, load from your trailer will be transferred to your vehicle. Consult this manual to determine how this reduces the available cargo and luggage load capacity of your vehicle.